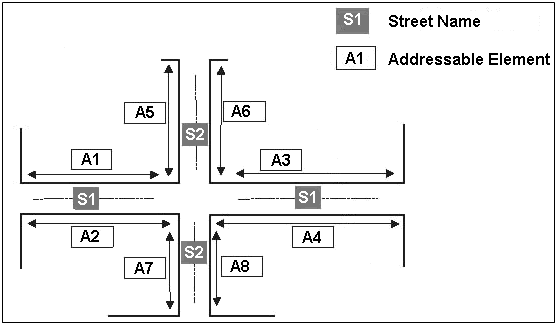
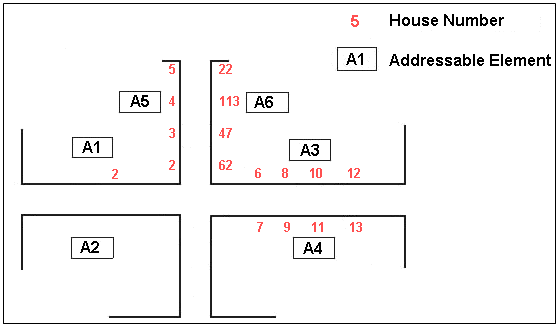
Addresses with Apartment BlocksFigure: Addresses with Apartment Block

- In the figure above, Apartment block BldgA has one entrance and has only one house
number assigned. In this case, the house number is assigned to addressable element A9.
- Apartment block BldgB also has only one entrance, but all house numbers residing in
this apartment block are even numbers 2 to 100. All of these house numbers are assigned
to addressable element A17, since A17 contains even numbers for the street.
- Apartment block BldgC also has only even house numbers. This block, however, has two
entrances. The first entrance is located at addressable element A18. In the gc table, if
this entrance gives access to house numbers 2 to 34, those numbers are stored in the
address attributes to the right side of the street. This street's left house numbers
(assigned to addressable element A20) are irregularly structured.
Note: If an apartment building has house numbers, but the addressable element in the
gc layer's R_STRUCT or L_STRUCT value is 0 (no structure), addresses is not
assigned to the Road Element.
Streets with Two Street Names
If a street has two street names, but only one official street name and one alternate
street name, the full house number range is assigned to both the official street name and
alternate street name. The street names are applicable to both sides of the streets.
If a street has two official street names and each of the street names belongs to only
one side of the street, and thus to only one Addressable Element, the record for the
Transportation Element is repeated, one time for each "Side of Line (SOL)," which for the
first record is set "1 (Left)," and for the second "2 (Right)."
Dead-End Streets
On a dead-end street, house numbers may not be well ordered, especially at the end of the
street. House numbers are allocated to the most appropriate Addressable Element.
Alpha-Numeric House Numbers
If a house number is alpha-numeric (e.g., 4a) this number appears as "4" in the gc
table's left or right first house number attribute field (L_F_ADD or R_F_ADD). This house
number is called the "Base House Number." The complete information "4b" is stored in a
separate Left (or Right) First Full House Number field (L_F_F_ADD or R_F_F_ADD).
Address IDs and Official Street Codes
The gc table fields L_ADDRID and R_ADDRID store stable, definitive TomTom® IDs that are used for joining information with a Transportation Element
or a group of Transportation Elements belonging to the same street (a unit with the same
Street Name). When a match is made between an Address ID and a geocoded Feature, the match
can be translated into a Relation of the Feature with the Transportation Element or the
street it belongs to. Official Street Codes are used by authorities in some countries for
identifying a street. Official Street Codes are stored in the sc (Official Street
Codes) table.