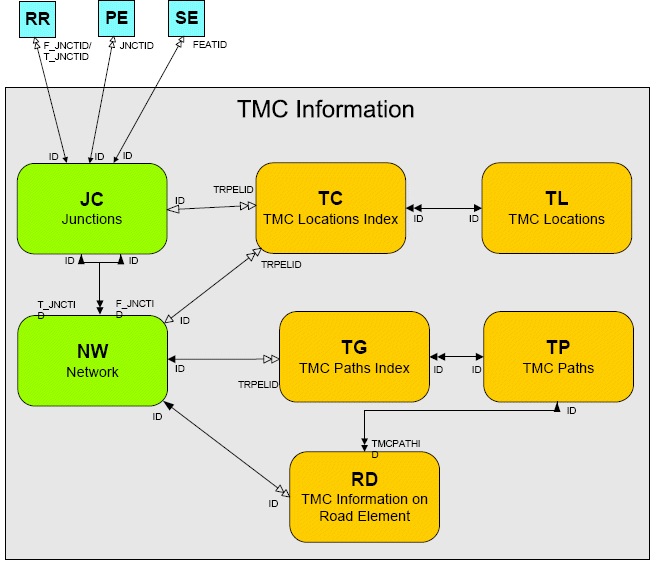
Restrictions and Maneuvers
Restrictions and Maneuvers are limitations to take into consideration when calculating a route.
Restrictions
| RESTRICTION TYPE | TABLE | ATTRIBUTE | COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Direction of a Transportation Element | nw, rs | Direction of traffic flow (ONEWAY)/ (RESTRTYP = DF) | Direction depends on the relative positions of the F_JNCTID and T_JNCTID of an Element. |
| Access to the F_JNCTID and T_JNCTID | nw, rs | Blocked passage at start or end of junction (F_BP; T_BP)/ (RESTRTYP = BP) | A physical obstruction to prevent vehicle access (e.g., to a Campground, School). |
| nw, rs | Private Road (PRIVATERD) | Road not open to public motorized vehicles. | |
| nw, rs | Construction Status (CONSTATUS)/ (RESTRTYP = 6Z) | Road closed for construction/maintenance. | |
| Time Restriction | td | Time Domain (TIMEDOM) | Closed for a measurable amount of time. |
| Vehicle Type | rs | Vehicle type restriction (VT) | The type of vehicle restricted. |
| Special Restrictions | rs | RESTRTYP = SR | Special restrictions include roads accessible by employees only, residents only, authorized personnel only, etc. |
Blocked Passages
- Vehicle Type (VT) Restriction - Defines the type of vehicle that the blocked passage applies to;
- • Validity Period (VP) Restriction - Defines the time period that the block passage is valid.
Removable Blockage
Removable Blockage is another attribute that can be applied to a road element in cases where TomTom can capture the method of bypassing the blockage (e.g., keyed access, guard controlled or accessible by emergency vehicles). If a road element does not have the removable blockage attribute, the blockage still may be bypassed due to the vehicle type or the validity period of the blockage as mentioned above.
Maneuvers and Routing
A Maneuver represents a mandatory, preferred or prohibited access of a Transportation Element, in relation to another Transportation Element.
See Maneuvers (mn) earlier in this user guide for descriptions.
| SEQNR | FEATURE | FUNCTION | RELATES TO |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transportation Element (Road or Ferry Element) | Element travelled on before arriving at a traffic sign indicating a maneuver. | ID in the nw table |
| 2 | Junction | Location of a traffic sign, where the maneuver actually begins. This is also the central reference point or anchor point to build a Maneuver Path (identified by its own ID). | JNCTID in the mn table; F_JNCT / T_JNCT in the nw table |
| 3 | Transportation Element | Element that is routed to, and for which the maneuver is valid coming from the first Element. | ID in the nw table |
| 4 | Transportation Element | Element for which the maneuver is valid, coming from the preceding Element (e.g., 3). | ID in the nw table |
Figure: Implicit Turn Maneuver in Map Display
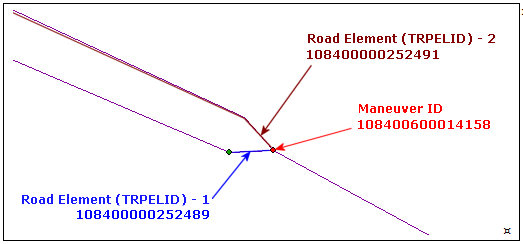
Figure: Implicit Turn in Tables
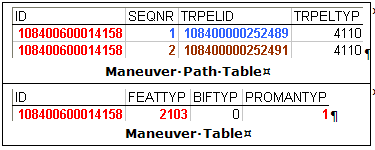
-
- The first Road Element (4110) in the maneuver path is 108400000252489.
- The second Road Element (4110) in the maneuver path is 108400000252491.
The Maneuver Table provides information defining the type of maneuver:
- The feature type (FEATTYP) 2103 = Prohibited Maneuver.
- The Prohibited Maneuver type (PROMANTYP) 1 = Implicit Turn.